Table of Contents
Definition of Drug Distribution In Hospital
Drug distribution in a hospital is defined as the physical transfer of drugs from the storage area in the hospital to the patient’s bedside.
This involves a series of activities like shipments, inventory control, payments, and accounts.
Drug distribution and prescribing systems are based upon prescription practices by the physicians, requisition by the nursing stations followed by transfer from stores for dispensing, packing, labeling, and distribution to inpatients and outpatients.
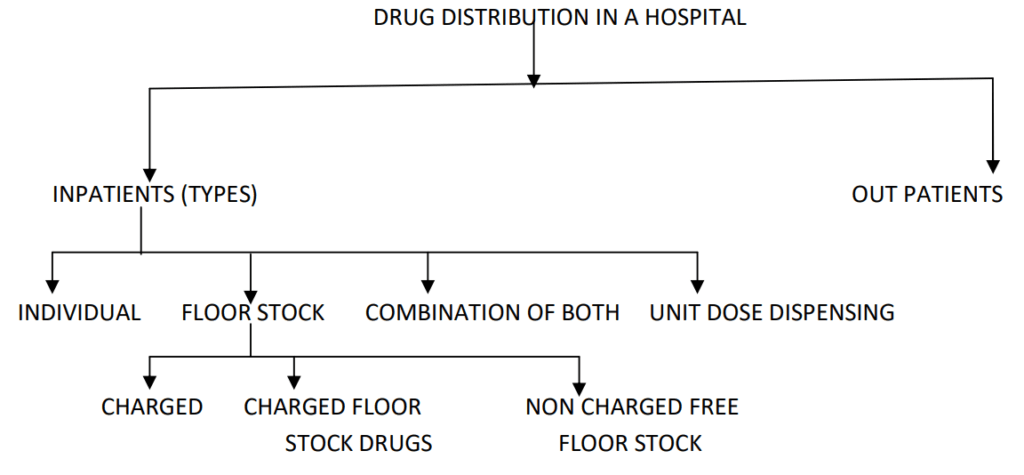
Types of Drug Distribution In Hospitals
The different types of drug distribution in a hospital are
- Individual prescription method
- Floor stock method
- Combination of individual and Floor stock method
- Unit dose drug distribution method.
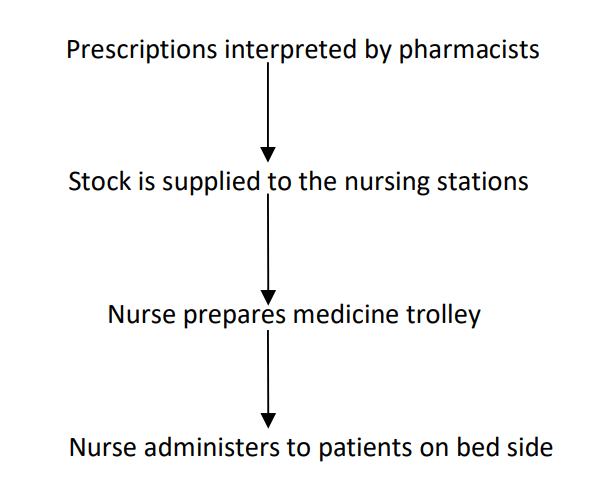
Individual Prescription Method:
This type of system is adapted in small hospitals where pharmacists are not available on the premises at all times.
The medications are compounded and dispensed similarly to those of other prescriptions.
The medicines required for treatment are dispensed in the pharmacy under the supervision of the pharmacist.
The medicines are labeled with the patient’s name, and location, and sometimes even the instructions for dosage are also written and sent to the nursing station.
Here the nurse is responsible for the administration of drugs for each of the patients.
Advantages:
- It provides closer interactions between the pharmacist, doctor, and the patient.
- It provides better control of inventory.
- Prescriptions are reviewed by pharmacists also.
Disadvantages:
- Increasing chances of wastage, mishandling, and even sometimes drug deterioration.
- Time-consuming process and drug distribution is delayed.
- Increased potential of medication errors due to lack of pharmacist supervision at the time of scheduling, drug distribution, and preparation and administration process.
FLOW PATTERN:
Floor Stock Method:
This method is also known as the complete ward stock system.
The drugs approved by the P& T committee are supplied from the pharmacy and are kept in the nursing station under the supervision of a registered nurse.
The drugs that are procured should have proven efficacy.
Medications under this are dispensed as
- Charged floor stock drugs
- Non–charged floor stock drugs.
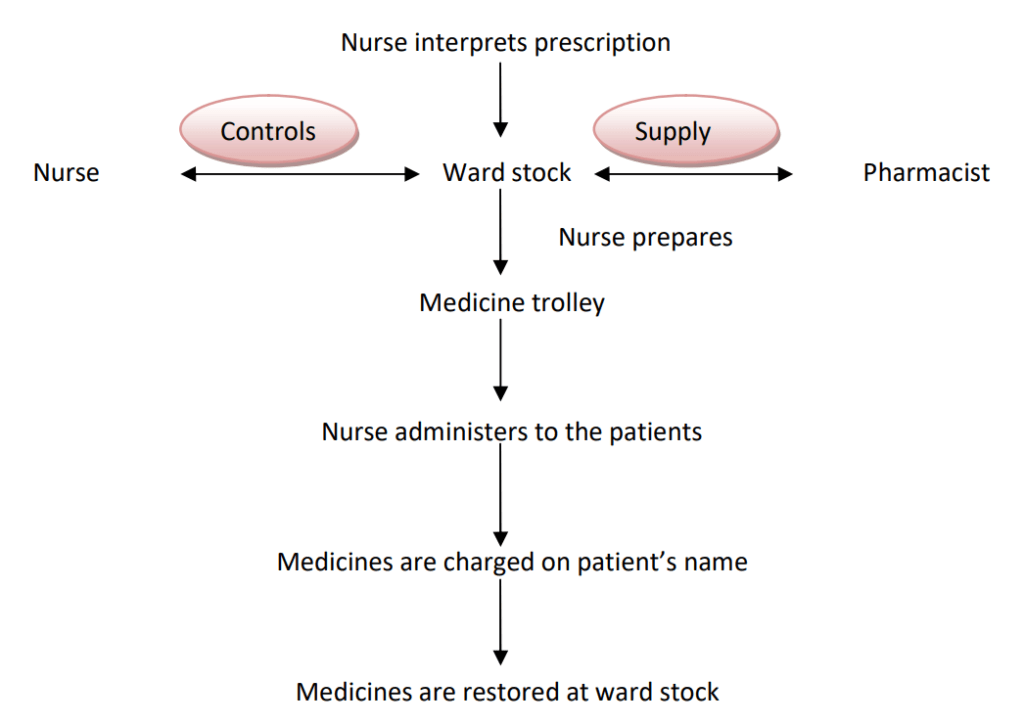
Charged Floor stock Drugs:
Charged floor stock is the medication that is available at each patient care area of the hospital for which a charge is made on the patient’s name after administration.
These medications are mostly injections and infusions.
The nurse indents the medication used at the nursing station to the patient at the inpatient pharmacy where billing is done and the medications are replaced at the patient care area again.
- Anti allergic – Hydrocortisones, sodium succinate.
- Anti-coagulants – Heparin, Warfarin
- Diuretics – Furosemide.
- Antacids – Mg.sulphate, ranitidine
- Spasmogenics – Neostigmine, Methyl sulfate.
- Others – paracetamol, Dextrose, DNS, Mannitol etc.
FLOW PATTERN:
Method Of Dispensing:
Charged floor stock medicines are dispensed by the Envelope method and Charged plate system methods.
Envelope Method:
In the envelope method pharmacist fills pre-labeled envelopes with specific drugs and orders a pre-determined quantity to the nursing unit.
Charged Plate Method:
In the charged plate system a plastic plate is prepared on the patient’s admission and every time the same plate is used for medication dispensing. After filling this is kept in the nursing unit.
The nurse prepares the required and sends it to the pharmacy where they are priced and forwarded to billing.
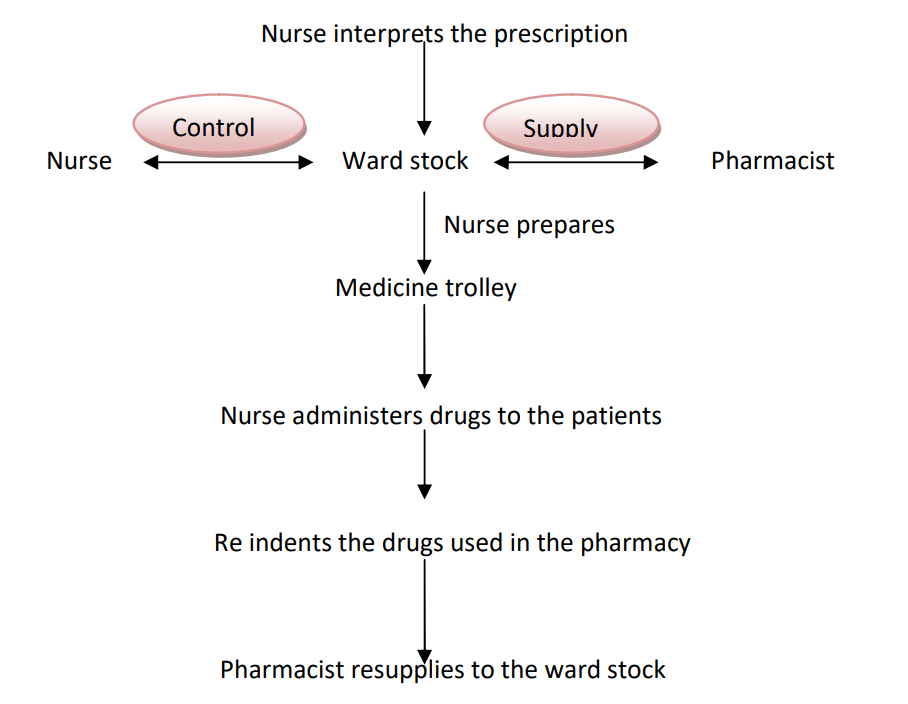
Non – Charged Floor Stock Drugs:
Usually, these items are inexpensive pharmaceutical materials that have universal patient use.
E.g.: Alcohol, Water for injection, Heparin, Lidocaine, etc.
Here the orders are received from patient care areas and the nurse is responsible for maintaining inventory control including requisition and returned medicines.
Adequate stocks can be kept based on the usage and the number of patients.
FLOW PATTERN:
Method of Dispensing:
The nurse takes the responsibility of dispensing the drugs. The nurse takes the responsibility of taking the medications from the inventories present at the nursing station.
The pharmacist inspects it and then gives it to the nurse. The nurse administers the medication.
The nurse re-indents the medication, pharmacist inspects and refills the medication used in the nursing cabinets.
Control Supply Here the dispensing of drugs is done in two methods
- Drug basket method
- Mobile dispensing unit method.
a) Drug Basket Method:
The nurse takes the responsibility of dispensing the drugs. Here the nurse on the night shift indents the medication to the pharmacy.
The nurse keeps all the empty bottles and containers along with the requisition in a basket and sends it to the pharmacy.
The pharmacist dispenses the medication according to the requisition and delivers it to the nursing station again.
b) Drug Dispensing Unit Method:
Here the medicines are dispensed by using a trolley. They are provided with a lock and key facility.
The pharmacist takes delivery to the nursing station. Each of the patients is identified with a name on a separate box.
Medicines are selected according to the prescriptions and the nurse administers them to the patients.
Advantages:
- Medicines are available readily to the patients.
- Minimal pharmacy workload.
- All information can be printed on labels hence easy to read and identify.
- No need to send prescription sheets to the pharmacy.
Disadvantages:
- Increased potential for medication errors.
- Limited capacity for proper storage of drugs in wardrobes.
- Increased stock of medications.
- Financial losses due to obsolesce and deterioration.
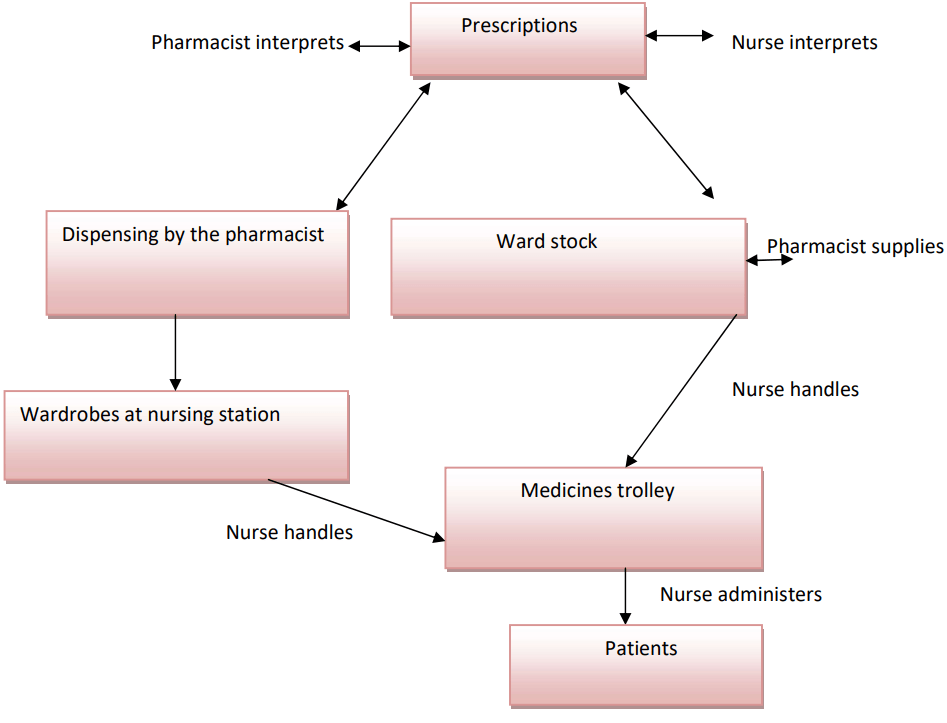
Combination of Both Individual and floor Stock Dispensing Systems:
Here medicines are supplied either as ward stocks or from floor stock dispensing for all the patients.
This is the most common method of dispensing.
FLOW PATTERN:
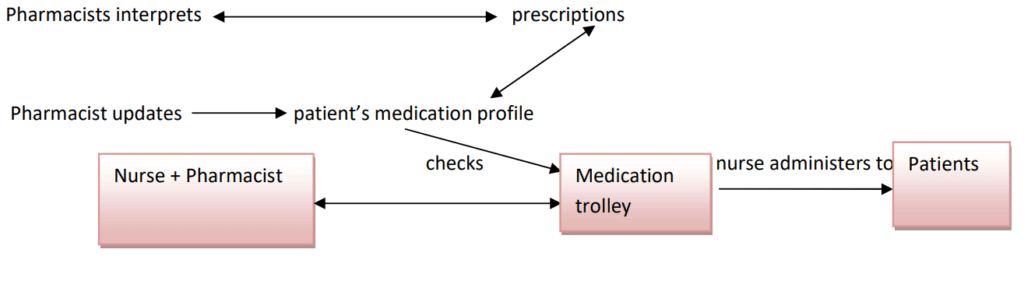
Unit Dose Drug Distribution System
This is the safest and most accepted method of dispensing medications to hospitalized patients.
In these systems, pharmacists prepare each dose of medicine ready for administration rather than issuing containers of medications to patient care areas where nurses must prepare medication for administration.
Here pharmacists are held responsible for educating nurses with concepts of unit dose dispensing systems. Here pharmacists use different models and techniques for the safe and effective distribution of drugs.
Advantages:
- It eliminates prescription label typing and labeling errors.
- The floor stock system of distribution is eliminated.
- Safe mode of distribution of drugs under pharmacist supervision.
- There is an accurate medication charge.
- It eliminates excessive duplication of orders and paperwork at nursing stations.
- It conserves storage space at nursing stations.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on: Roles And Responsibilities of Hospital Pharmacist
