Definition Of Hospital
A hospital is an institution that provides diagnostic and therapeutic facilities by trained personnel to facilitate the work of a physician in his/her primary position relating to the care of ill or injured people.
It can also be defined as an institution or a medium through which expert staff and other health care agencies direct their activities by providing quality services in the improvement of public health.
It is mainly a service-oriented sector and trained personnel include pharmacists, nurses, laboratory technicians, and dieticians.
FUNCTIONS OF A MODERN HOSPITAL:
A modern hospital is much more than a healthcare institution. The important functions of modern care hospitals are:
- Patient care
- Public health
- Education
- Research
The other functions include
- It raises the quality of care and general standards of medical practice.
- It lowers the incidence of disease through early detection of a disease and its intermediate treatment.
- It also provides raised income and social status.
- It acts as an immunization center in preventing epidemic, endemic, and pandemic diseases.
- Bigger hospitals help in the growth of medical sciences by training doctors, nurses, pharmacists, and other medical staff.
- It acts as a link between the general public and the policymakers i.e. government.
CLASSIFICATION OF HOSPITALS
Hospitals are classified in a number of ways based on various criteria like
- Type of services
- Length of stay
- Bed capacity
- Owner stay.
They may be grouped according to clinical and non-clinical orientations.
TYPES OF HOSPITALS
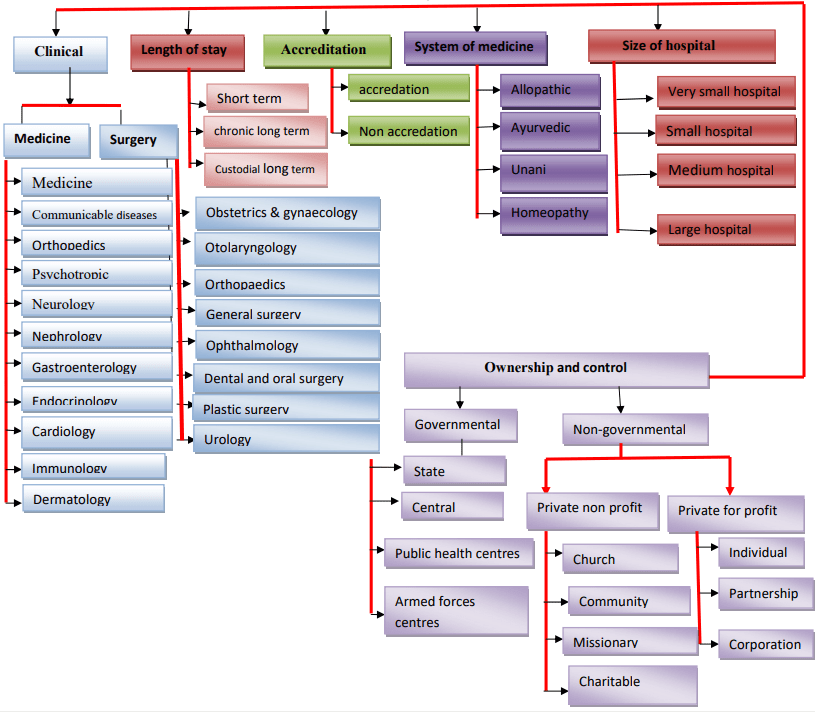
A. CLASSIFICATION BASED ON THE SYSTEM OF MEDICINE ADOPTED:
They are:
- Allopathic hospital
- Ayurvedic hospital
- Siddha hospital
- Unani hospital
- Homeopathic hospital
- Physiotherapy hospital
- Nature’s Cure Hospital.
B. CLASSIFICATION BASED ON CLINICAL ORIENTATION:
The word clinical refers to the treatment of diseases in human beings. Different types of diseases need different ways and methods of treatment. Hospitals are classified according to
- TB hospital
- Leprosy hospital
- Cancer hospital
- Psychiatric hospital
- Maternity hospital
- Infection and communicable disease hospital
- Drug addiction rehabilitation center.
C. CLASSIFICATION BASED ON ANATOMICAL – PHYSIOLOGICAL SPECILAZATIONS:
- ENT hospital
- Orthopaedic hospital
- Ophthalmic hospital
- Neurology hospital
- Nephrology hospital
- Cardiothoracic hospital etc.
D. HOSPITALS BASED ON ACCREDITATION:
According to the Joint Commission on accreditation of health care organizations (JACHO)
these are
a) Long-term health care facility: Facility for inpatient care other than hospital.
b) Resident treatment facility: Facility providing safe, hygienic arrangements for residents including preventive, rehabilitative, social, spiritual, and emotional care.
These are again divided into
a) Clinical – Ambulatory patients seen by appointment & treated by a group of physicians.
b) Ambulatory surgery center – Patients here are admitted for surgical procedures till their discharge.
E. CLASSIFICATION ON THE BASIS OF OWNERSHIP:
On the basis of ownership, hospitals are again divided into governmental and non-governmental institutions.
- Governmental – Armed forces, ESI hospitals, state–urban and public health care centers.
- Nongovernmental – church-related missionaries, charitable etc.
F. CLASSIFICATION BASED ON BASIS OF BED CAPACITY:
On the basis of bed capacity hospitals are classified into
- Under 50 beds
- 50-99 beds
- 100-199 beds
- 200-299 beds
- 300-399 beds
- 500 beds and above.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on: Gastro retentive drug delivery systems
