Cosmetic excipients are the ingredients used in the formulation of products like hair care, skin care, sun care, cleaning, make-up or oral care, toiletries, cosmetics, and fragrances.
Table of Contents
Function of Excipeints:
- Improve the quality of the product.
- Product harmful effects of UV rays.
- Surfactants provide cleaning and foam-building properties in shampoo and body washes.
- Preservatives prevent contamination of products.
- Provide stability of the product.
Ingredients of Cosmetics
- Water
- Oils, Fats, Waxes
- Humectants
- Surfactants
- Preservatives
- Rheology modifiers
- Perfumes And Colors
- Herbal or Plant Material
Surfactants
Surfactants lower one or more boundary tensions at the interface in the system. One common feature of surfactants is that they are all molecules containing a hydrophobic part & a hydrophilic part. Used in cosmetics to impart the following functions.
- Detergency
- Wetting
- Foaming
- Emulsification
- Solubilization
a) Detergent: Where the main problem involves the removal of soiling matter, surface active agents with detergent properties are needed, for example in shampoos.
b) Wetting: In products where good contact is required between a solution and a substrate, good wetting properties are required, for example in the application of hair colorants and permanent waving lotions.
c) Foaming: Some products need to have a high level of foam in use, and for these products, special surface-active agents are used, for example in shampoos and foam baths.
d) Emulsification: In products where the formation and stability of an emulsion is a vital feature, surface-active agents with good emulsifying properties are required, for example in skin and hair creams.
e) Solubilization: Products in which it is necessary to solubilize an insoluble component need surface-active agents with good appropriate properties, for example, the solubilization of perfumes and flavors.
Classification Or Types of Surfactants
Anionic: Fatty acid soaps, alkyl sulfates, alkyl sulphonates, polyethylene glycol ester, alkyl ether sulfates taurines, sarcosinates, etc.
Cationic: Alkyl trimethyl ammonium salts, Dialkyl dimethyl ammonium salts, alkyl pyridinium salts, quaternion diamine salts.
Non-ionic: alkanol amides, alkyl polyglycol ether, thioethers, alkyl polyethylene imine amides.
Ampholytic: Betains, alkyl imidazolines, acyl peptides, etc.
How surface tension works
Surface tension effects
- Surfactants lower the surface tension of water by reducing the energy at the air/water interface.
- This surface tension reduction allows water to better-wet surfaces for effective cleansing action. The concentration of surfactants is higher at the surface than in solution.
Foam generation
- Foam is generated when air is trapped beneath a liquid surface containing surfactant molecules.
- The physical action of rubbing a surfactant solution onto the hair or body with the hands helps create pockets of air.
- Anionic surfactant solutions create the greatest volume of foam.
- When amphoterics used as primary surfactants, the foaming character is not great, but when combined with anionics the effect is quite good with regard to foam generation.
Applications of Surfactants
Creams and lotions
- Surfactants are mainly used as emulsifiers in creams and lotions.
- Emulsifiers not only allow the emollient oils to peacefully coexist but also have an impact on the appearance of an emulsion.
- Use levels are generally from 1% to 5%, and generally are anionic or nonionic, though cationic is used as well.
- Soaps and phosphate esters are the primary anionic surfactants employed
Shampoos
- Surfactants perform the cleansing and foaming of shampoos.
- In addition, the viscosity and flow characteristics are dictated by the selection and interaction of the surfactants.
Skin cleansers: Skin cleansers viz., hand wash formulations tend to use anionic sulfonates as well as sulfonates.
Conditioners: Most hair conditioners are built with a long-alkyl-chain cationic surfactant for conditioning, a fatty alcohol for viscosity, and a nonionic ethoxylated fatty alcohol for emulsion stability.
Color cosmetics: Surfactants are used as emulsifiers and dispersants in such color cosmetics applications as liquid foundations and mascara.
Antiperspirants: Surfactants are not an integral element of stick antiperspirant formulations, but at times used to enhance the washability of formulations from the skin and fabrics.
Rheology Modifiers
Definition
- Rheology modifiers are additives that are primarily used to increase the viscosity or impart a desired rheological profile to a formulation.
- However, they can sometimes be multifunctional and perform secondary roles such as gelling agents, emulsifiers, conditioners, or film-formers and thickeners.
CLASSIFICATION
Natural rheology modifiers
1) Polysaccharides:
a) Natural anionic: Ex: Alginates (Alginic Acid), Pectin, Xanthan Gum, Spinosa gum, Carrageenans.
b) Natural cationic: Ex: Chitosan.
c) Natural nonionic: Ex: Starch
d) Natural amphoteric polysaccharides: Ex: Carboxy methyl chitosan, chitosan
2) Semi-natural
- Semi-natural anionic: Ex: Cellulose gum (Sodium Carboxymethylcellulose)
- Semi-natural cationic: Ex: Hydroxy ethyl cellulose (HEC)
- Semi-natural nonionic: Ex: Cellulose ethers (HPC), Methylcellulose, EHEC
3) Synthetic rheology modifiers
Synthetic rheology modifiers are produced by polymerization of various types of monomers.
Ex: Modified sulfonic acid (AMPS®) polymers,
Alkali swellable emulsion polymers,
Polyacrylic acid polymers (carbomer)
Applications of Rheology Modifiers
Natural Rheology Modifiers
- Alginate is used in cosmetic skin care preparations such as creams, lotions, pastes, etc.
- Alginates are also used as gelling agents and stabilizers in cosmetic emulsions and gels. It helps in retaining the color of lipstick on the lip surface by forming a gel network.
- Pectin is used as a thickener, emollient, and stabilizer in hair tonics, body lotions, shampoos, and conditioners.
- Used as structure provider in pastes, ointments, oils, and creams.
- Xanthan gum is a thickener, and stabilizer and offers excellent suspending properties. Used in personal care products such as shower gel and shampoo.
- Spinosa gum is used as a thickener in baby hygiene and cleansing cosmetics.
- Carrageenans used as gelling agent and thickener .
- Starch is primarily used as an emulsion stabilizer, thickener, and rheological modifier in cosmetics.
Semi Natural Rheology Modifiers
- Cellulose gum is used as a film-forming, emulsion stabilization, and thickening agent in skin care cosmetic preparations.
- Sodium carboxymethylcellulose is used as a viscosity modifier in cosmetic skin care preparations viz., skin care creams, skin whitening creams, face powder, and sunscreen creams.
- Polyquaternium-10 is used as a conditioner in shampoo
- Hydroxypropyl cellulose is designed for use in personal care applications as a thickening and stabilizing agent. Used as a rheology modifier in hand sanitizers.
- Hydroxy propyl methylcellulose effectively thickens conditioners, lotions, creams, hair preparations, and topical gels.
Synthetic Rheology Modifiers
- These polymers have been used in hair styling gels, shower products, shampoo, face/neck care, body care creams, liquid body soaps, hair colorants, hair treatments, shaving gels, liquid hand soap, etc.
- Polyacrylic acid polymers are used in a variety of aqueous formulations including personal care, cosmetic care, home care, pharmaceutical, and other industrial applications.
Humectants
- Humectants are hygroscopic materials that have the property of absorbing water vapor from moist air until a certain degree of dilution is attained. The key characteristic of a humectant is hygroscopicity.
- Hygroscopicity is the ability of a material to hold (or bind) moisture to itself. A useful humectant will retain moisture over a wide range of humidity conditions and for an extensive time period.
Ideal Properties
- A humectant should be able to absorb a great deal of moisture from the atmosphere and retain it under normal conditions or at a broad range of relative humidities.
- Its moisture content should change little when exposed to large changes in relative humidity.
- A humectant should be nontoxic, nonirritant, and compatible with a wide range of raw materials.
- A humectant should exhibit good color, odor, and taste properties.
- A humectant should be of low viscosity to facilitate incorporation into systems.
- A humectant should be nonreactive with commonly used materials, and it should be non-corrosive to commonly used packaging.
- A humectant is nonvolatile and should not solidify nor deposit crystals under normal temperature conditions.
- A humectant should be readily available and relatively low in cost.
Classification/Types
1) Inorganic Humectants
- These are salts of inorganic acids.
- Ex: Calcium chloride is an example of this class.
- There is currently little use for this class of humectant in personal care formulations.
- They have problems related to their corrosive effects and incompatibility with other raw materials.
2) Metal-Organic Humectants
- The metal-organic class of humectants is much more useful.
- These materials, which contain a mixture of a metal ion and an organic portion, are usually the salts of strong bases and weak organic acids.
Ex: Sodium lactate and sodium PCA (pyrrolidone carboxylic acid).
3) Organic Humectants
- This class is the broadest and the most widely used in personal care formulation. These materials are typically polyhydric alcohols and their esters and ethers. Ex: Glycerin, propylene glycol, sorbitol, Polyethylene Glycols, Sodium Pyrrolidone Carboxylate (Na-PCA).
4) Miscellaneous Humectants
Ex: Tropocollagen, keratins, glucose ethers and esters.
Applications of Humectants
Skin creams, ointments, and lotions using humectants
- Humectants used in creams and lotions at levels of 1-5% typically prevent surface dehydration of the product when exposed to air.
- In some creams, glycerin is used at a 10% loading to enhance the moisturization/moisturization of the skin.
- Glycerin is traditionally used as an active ingredient in hand and body creams because it tends to reduce roughness, which is due predominantly to the dehydration of the uppermost levels of the stratum corneum.
- The mixture of glycerin, sodium lactate, urea, and collagen incorporated into a formula, significantly improves the suppleness of skin.
- Sorbitol is probably the best in this regard, followed by propylene glycol and glycerin, it reduces flaking.
- Sorbitol normally produces a soft, velvety feel, while propylene glycol is somewhere between glycerin and sorbitol.
- Polyethylene glycols are toxicologically inert, as exemplified by their use in a USP PEG ointment. This is a 1:1 mixture of PEG-400 and PEG-4000 and is used as a water washable ointment.
Hair applications for humectants
- Humectants are typically added to shampoos, body washes, and bath and shower gels at 2-5%.
- They also help to reduce the cloud point of the product, ensure clarity in cold temperatures, and help to prevent cracking.
- Humectants tend to reduce the foaming of surfactant systems.
Glycerin is a good dispersing agent for pigments in foundation makeups and lowers the freezing point of lotions and shampoos.
Emollients
Definition
- Emollients are the excipients that prevent moisture evaporation from the skin by forming or creating a thin layer on the skin.
- It maintains the moisture content on the skin and its flexibility.
Classification or Types of Emollients
Hydrocarbons:
Ex: Squalane, Liquid paraffin, Vaseline, Poly isobutene, Microcrystalline wax, Paraffin wax.
Natural Oils:
Ex: Common vegetable oils olive oil, avocado oil, sesame oil, almond oil, rice bran oil, safflower oil, castor oil.
Fatty acid esters:
Fatty acid esters are synthesized by dehydrating fatty acids and alkyl alcohol and have a conditioning effect of softening the skin to create a smoothing sensation.
Ex: Isostearic acids and other liquid oils, Fatty acid ester of poly glycerine.
Lanolin, Lanolin derivatives, Sterol esters
- Lanolin is a semisolid oil with a complex composition of cholesterols and many long-chain hydroxy acid esters found in sheep sebaceous glands.
- used in skin creams and lipsticks, and is an emollient with a high water-holding property cosmetics.
Aliphatic higher alcohol and fatty acids
- Aliphatic higher alcohols and fatty acids are not effective emollients when used alone, but they show emollient effects when used with hydrophilic surfactants.
Ceramides
- These are composed of 15% cholesterol ester, 5% cholesterol, 5% fatty acid, and 5% sugar ceramide.
Water soluble oils
- These oils independently have moisture-retaining properties but are also used to reduce the stickiness of glycerin.
Applications of Emollients
- Emollients are used in cosmetic formulations for different purposes viz., skin softening; occlusive moisturization; lubrication; and structure formation in emulsion viscosity.
- Emollients are traditionally used for all kinds of skin diseases.
- Emollients are ingredients that soften skin and seal in moisture, creating an occlusive, protective barrier on the surface.
- Emollients are effective for soothing and healing dry skin due to almost any cause, including viz., eczema, psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, hypothyroidism, diabetes, and kidney disease.
- Emollients are used in other skin irritations conditions such as burns from radiation treatments and diaper rash.
- Emollients used to treat dry skin caused due to hot water showers; long showers; exposure of hands to water for long periods during cleaning or washing dishes;
- exposure of skin to closer to strong heat; usage of harsh drying soaps and cleansing products and excessive sun exposure.
- Emollients are used no matter what the cause for skin, which is dry, itchy, irritated, cracked, and uncomfortable, even worse openings of skin due to scratching or cracking can bleed, or become infected.
- Emollients used to soften cracks, improve the skin’s barrier function
- A class of hydrocarbons viz., squalane, penta hydrosqualenes, liquid paraffin, vaseline, poly isobutene, and paraffin wax were used as emollients in various cosmetic preparations such as hair conditioners, skin protection creams, skin protection lotions, skin ointments, eye shadows.
- A Class of natural vegetable oils viz., olive oil, avocado oil, sesame oil, almond oil, rice bran oil, etc animal fats and oils viz., beef tallow, horse tallow, and egg yolk oil used as emollients in hair care and skin care cosmetic preparations.
- Isostearic acids, branched fatty acids, and unsaturated fatty acids commonly used as emollients, are added to skin creams to adjust the application of softness and touch.
- Lanolin and its derivatives are used as emollients in skin creams and lipsticks and act as an emollient with a high water-holding property.
Preservatives
Definition:
Preservatives are the additives added to cosmetic products to prevent spoilage, prolong the shelf life of the product, and protect the consumer from the possibility of infection.
Ideal requirements
- Freedom from toxic, irritant, or sensitizing effects at the concentrations used on the skin, and mucous membrane.
- Stability to heat, moisture, dryness, and prolonged storage.
- Free from gross incompatibility with other additives used in cosmetic formulations and with the packaging material.
- Should be active at low concentrations and retain its effectiveness over a wide range of pH
- Should be effective for a wide range of microorganisms.
- Should be non-volatile.
- Should be readily soluble in its effective concentration.
- Freedom from causing negative attributes, such as products‟ odor, and color.
CLASSIFICATION
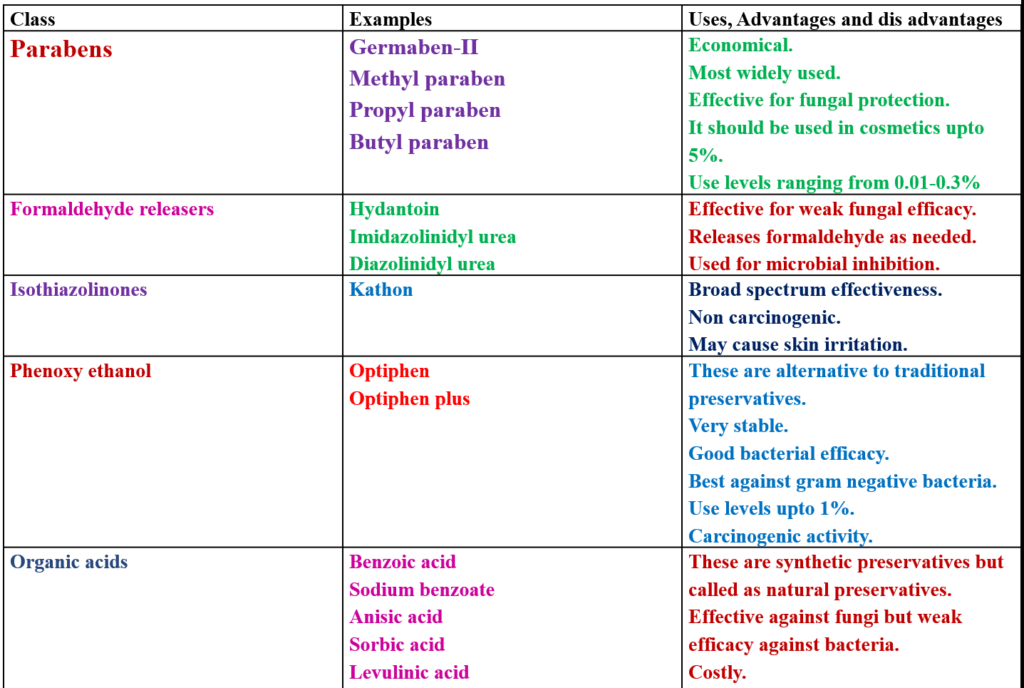
Applications
A preservative is a synthetic/chemical or natural ingredient with antimicrobial properties that is added to cosmetics and personal care products to maintain microbiological quality.
- Preservatives are used to increase the shelf life of these formulations, inhibiting the growth of microorganisms.
- Preservatives in cosmetics and personal care products help prevent contamination and the growth of harmful bacteria in products ranging from sunscreens, lotions, and shampoos to cleansers, toothpaste, and makeup.
- Antimicrobial preservatives in cosmetics and personal care products help prevent the growth of molds, yeasts, and bacteria, guarding against contamination that can cause irritation or infections.
- Antioxidant preservatives also can help keep personal care products from spoiling by suppressing reactions that can occur.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on: Cosmeceuticals as OTC drugs
