Definition of the tissue:
A tissue is a group of cells, similar in origin, structure, and function. This group of cells functions together to carry out specialized activities.
According to the structure and functions body tissues can be classified into:
- Epithelial Tissue.
- Muscle Tissue.
- Connective Tissue.
- Nervous Tissue.
- Nervous Tissue.
Table of Contents
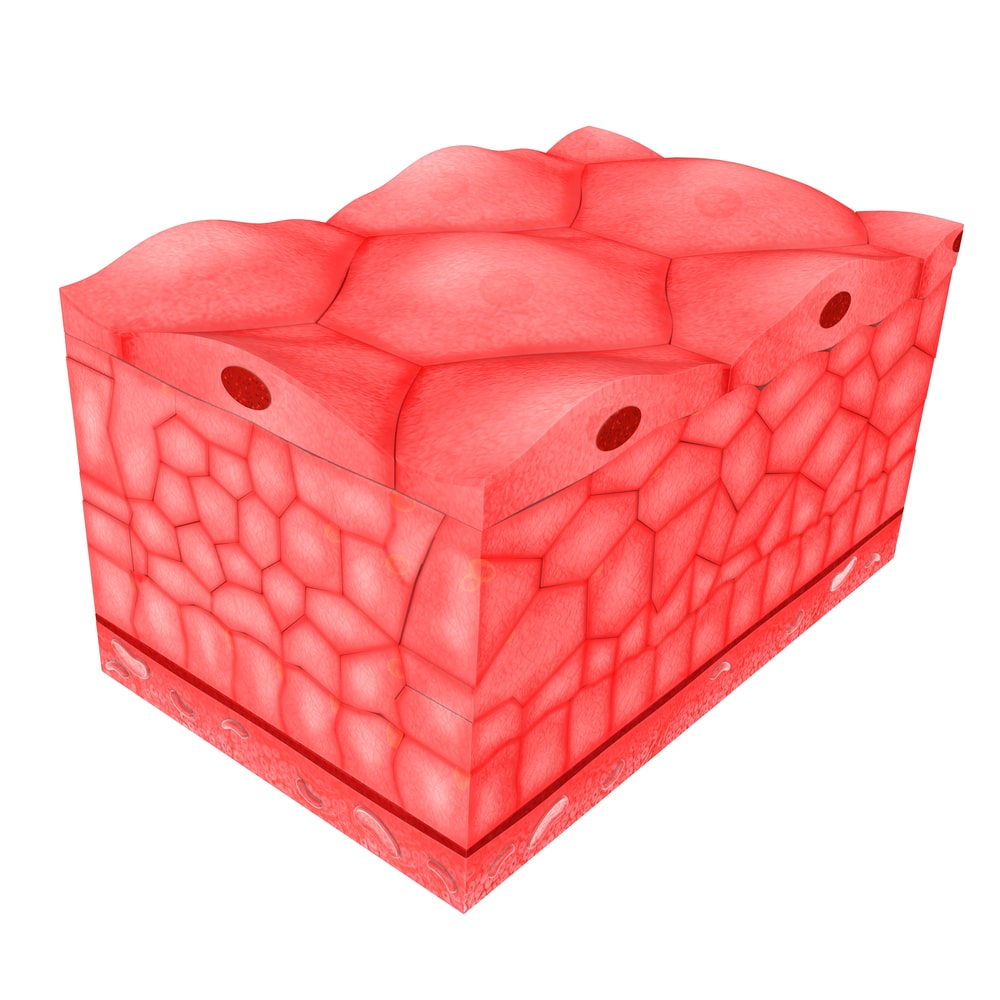
Epithelial Tissue
It is a tissue that covers an external and internal surface of the body or an organ It consists of cells that are situated very near to each other with the least intercellular spaces.
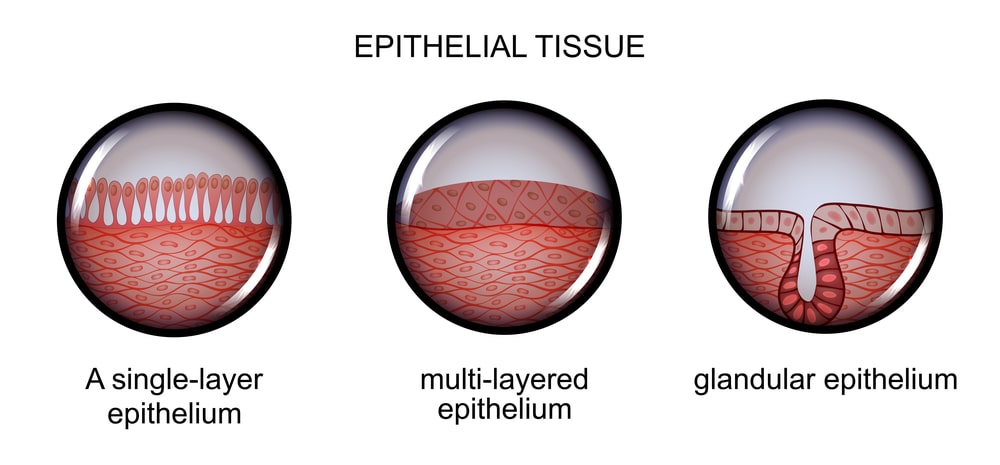
Functions of Epithelium: Protects the underlying tissues from friction and injury It helps in absorption, excretion, and secretion.
Classification of Epithelial Tissue :
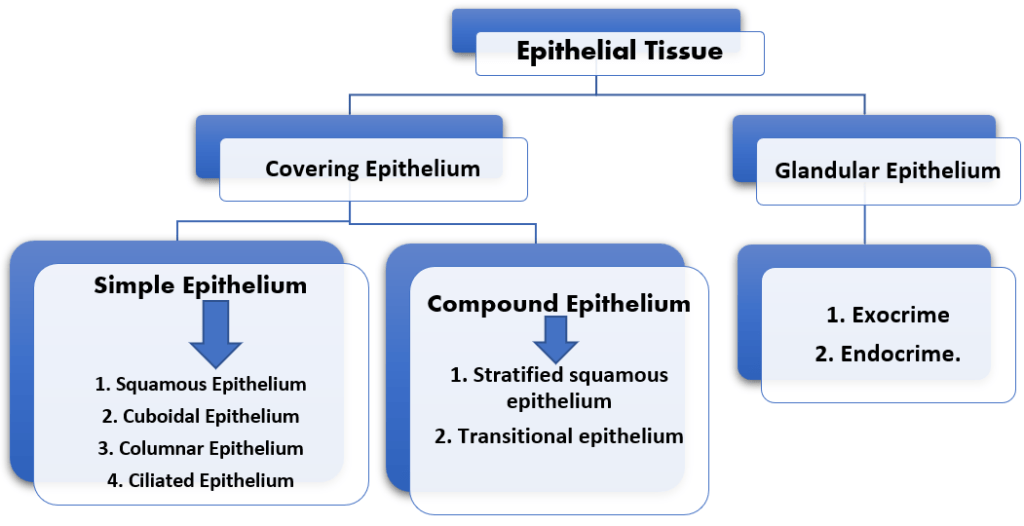
Simple Epithelium:
The cells of simple epithelium form a single layer of cells of various sizes and shapes and are further divided into Squamous, Cuboidal, Colmnar, and Ciliated epithelium.
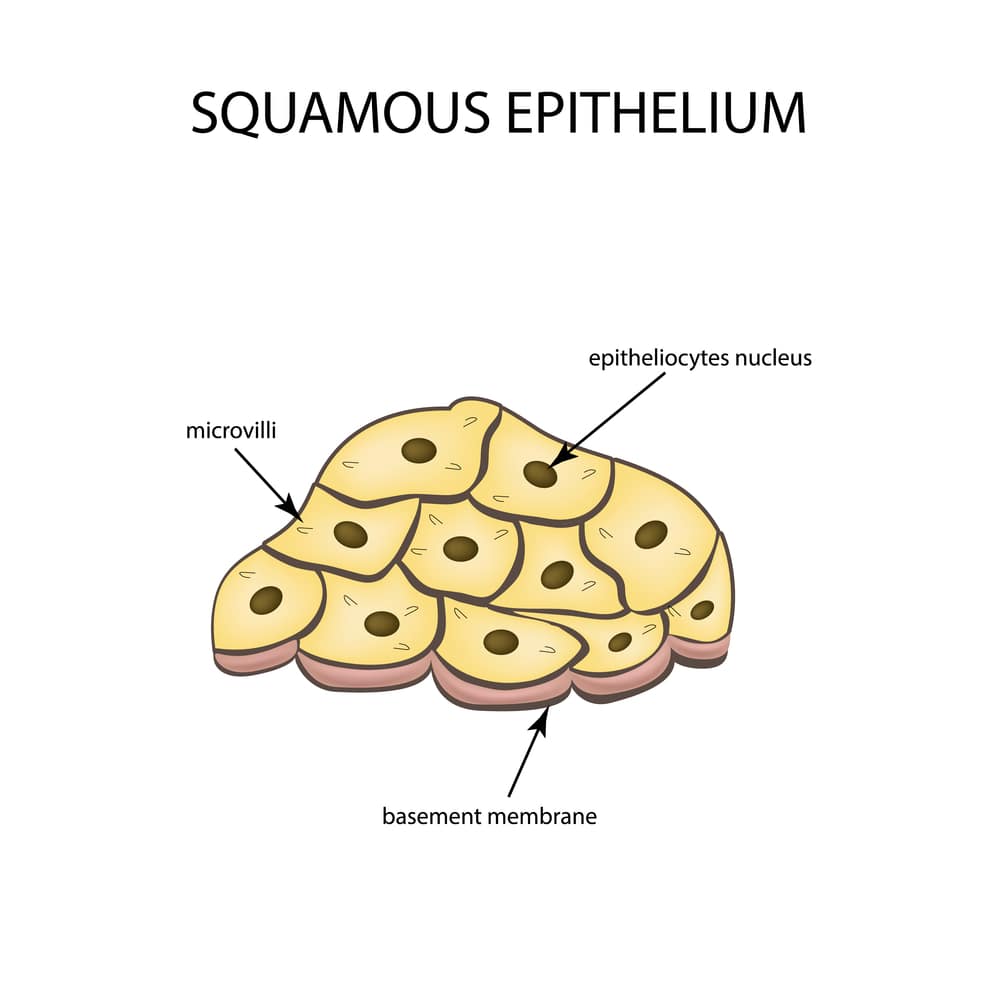
Squamous Epithelium:
- Squamous epithelial cells are also called “pavement epithelial cells because they are flat. The cells appear like tiles on the floor.
- Each cell has a polygonal shape and is filled with cytoplasm, the nucleus is usually placed in the center.
- It is found in the Lungs, Bowman’s capsule, Heart, Inner walls of the blood vessels, etc.
- It helps infiltrate and exchange gases and other substances from the blood.
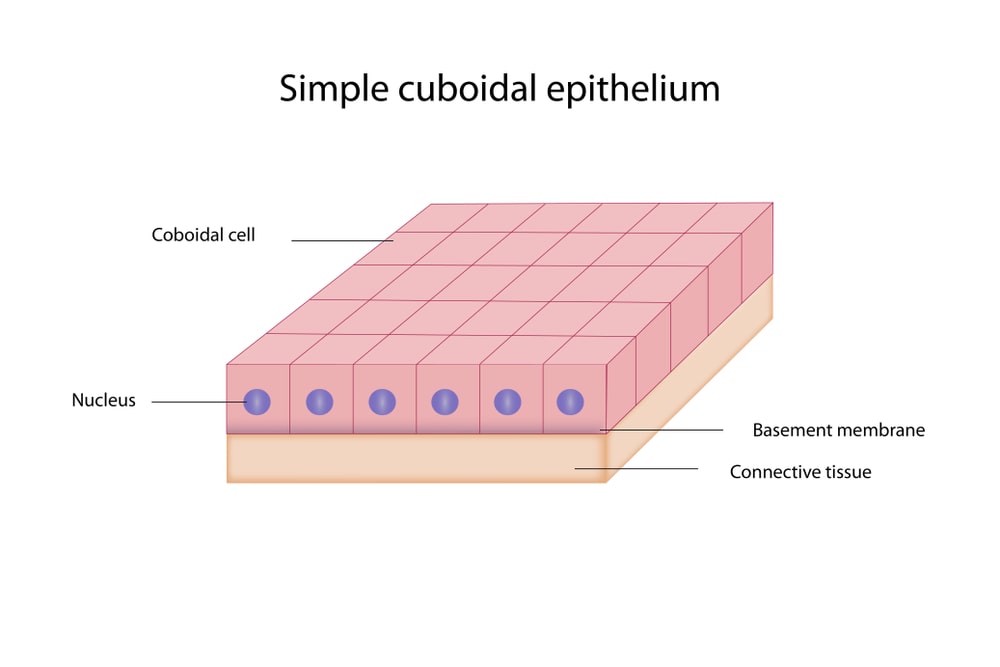
Cuboidal epithelium:
- This consists of cube-shaped cells lying closely together on a basement membrane, and have the same dimensions from all sides.
- Cuboidal cells are found in Bronchioles, Thyroid gland, etc.
- They help in the protection and secretion of various substances.
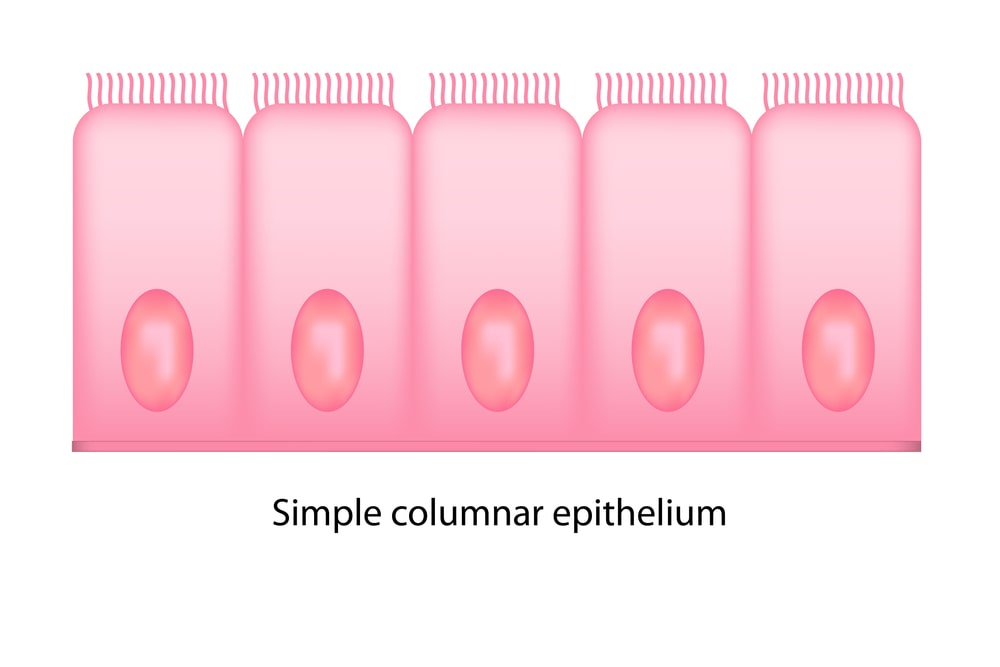
Columnar epithelium:
- Columnar epithelial cells are elongated cells, the height of which is more than the breadth. The nucleus is prominent but has a variable location inside the cell.
- It is found in the alimentary canal, lungs, and ducts of the glands.
- They help in the absorption and secretion of various substances
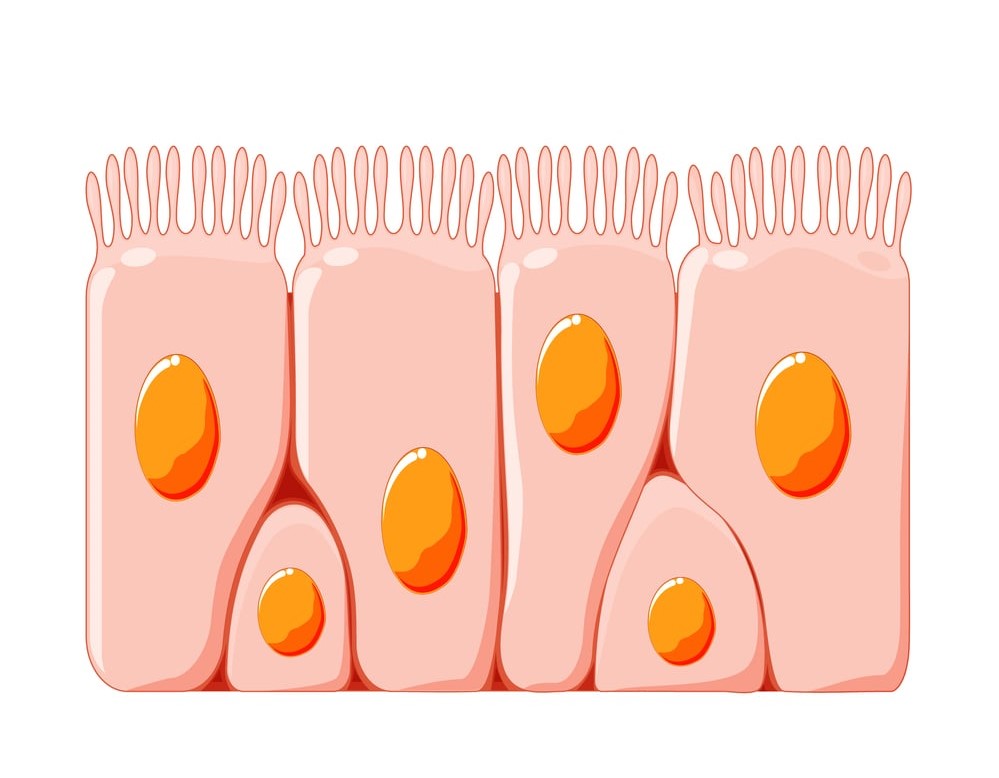
Ciliated epithelium:
- Cells of the ciliated epithelium may be columnar or cubical and consist of about 15-25 hair-like structures on the cell and are known as cilia.
- They are found in the respiratory tract i.e. trachea, bronchioles, nasal lining, oviducts, and uterus.
- They help in the flow of mucus, suspended particles, and bacteria.
Compound epithelium:
It is a type of epithelial tissue having more than one layer of epithelial cells. They are again classified into the stratified squamous epithelium and transitional epithelium.
Stratified epithelium:
- A stratified epithelium consists of several layers of cells of various shapes, basement membrane is usually absent.
- The main function of stratified epithelium is to protect underlying structures from wear and tear.
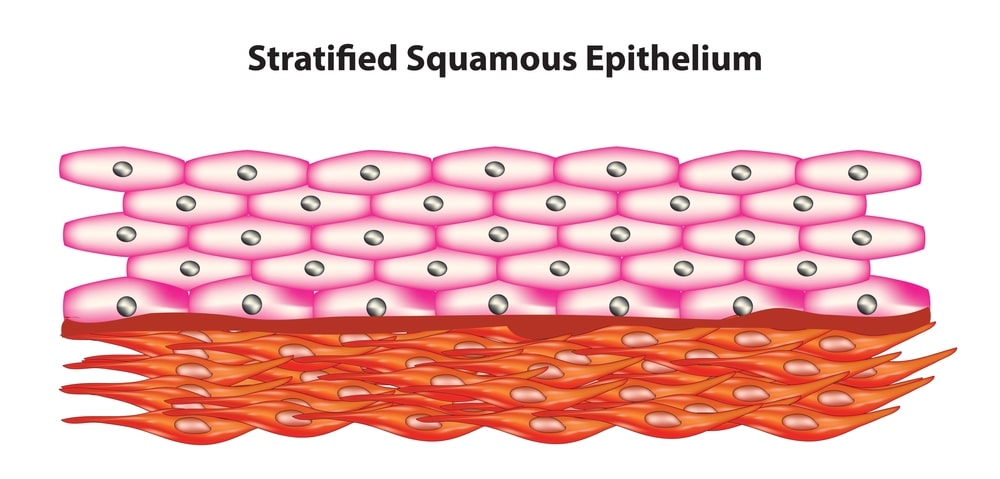
Stratified squamous epithelium:
- It is composed of several layers of cells of different shapes, in the deepest layer the cells are mainly columnar and they grow towards the surface, they become flattened and are then shed.
Non-keratinized Stratified epithelium:
- It does not contain keratinized cells and is found on wet surfaces subjected to wear and tear and is protected from drying.
- It is found in various mucus membranes such as the mouth, esophagus, pharynx, anal canal, vagina, cervix of the uterus, conjunctiva of the eyes, etc.
Keratinised Stratified epithelium:
- It consists of dead epithelial cells that contain the protein named keratin, it forms a tough waterproof protective layer that prevents the drying of the live cells underneath.
- They give protection against the atmosphere, mechanical pressure, friction, and injury.
- They are found in skin, nails, and hair.
Transitional epithelium:
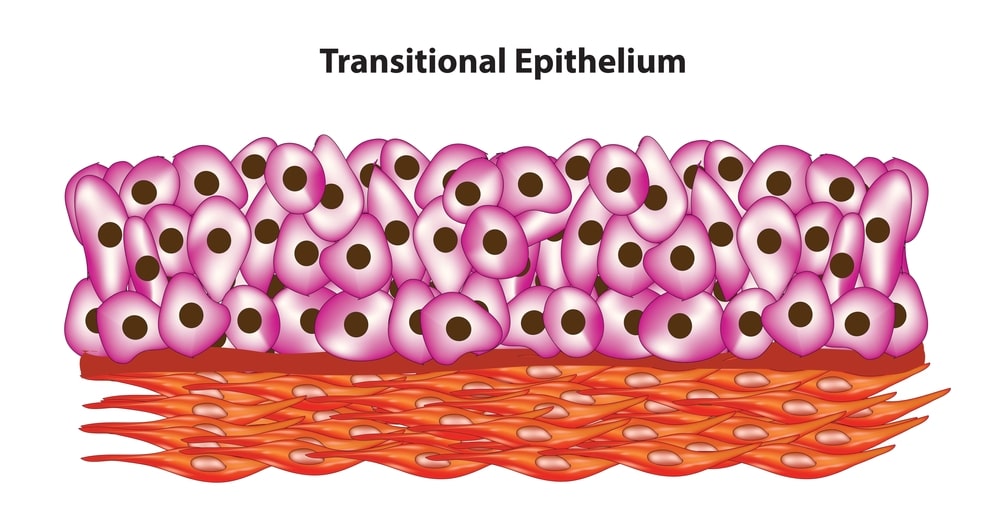
It is made up of pear-shaped cells. It is found in the pelvis of the kidney) ureters, urinary bladder, urethra, etc.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on: Ultra Structure of Bacteria