Hair colorants are hair care cosmetic products used for coloring the hair and work by bringing chemical changes in the natural hair. These are widely used by both genders to alter their natural hair color or add a new color.
Several reasons for using hair colorant products are to cover gray hair, to change to a color of more fashionable or desirable, or to restore the original hair color after it has been discolored by hairdressing processes or sun bleaching.
Ideal Properties of Hair Coloring Products
The ideal properties of typical hair coloring product
- Must impart stable color to the hair and color evenly.
- Should not color the skin.
- Gentle to the hair and scalp, does not dry or damage it
- Easy to spread and rinse off from the hair.
- Permanent dyes should have a long-lasting coloring effect.
- Should not lead to loss of the natural shine of hair.
- The shaft of the hair must not be damaged.
- The natural moisture of the hair must be maintained.
- Should be non-irritant, non-toxic, and non-sensitizing.
The technical qualities of hair coloring products
- Strong coloring power
- Appropriate rheological properties
- Appropriate pH
- Long-term stability
- Dermatological safety
CLASSIFICATION OF HAIR COLORANTS
Hair coloring products can be mainly categorized into two types based on the presence or absence of the chemical reaction (known as oxidation process) involved in the hair coloring process and also according to their duration of action in the hair.
Oxidative hair dye: These hair coloring products work based on an oxidative chemical reaction.
- Permanent hair dyes,
- Demi-permanent dyes,
- Hair bleaches.
Non-oxidative hair dyes: These are hair coloring products that do not contain oxidizing agents.
- Temporary dyes
- Semi-permanent dyes
- Additional hair dye products are also available known as progressive hair dyes, which are permanent but not oxidative.
(a) PERMANENT HAIR DYES: The color produced by these colorants last longer when compared to semi-permanent colorants. They contain a higher amount of oxidizing agents and have a highly alkaline pH compared to demi-permanent dyes, which make them permanent. These dyes may cause allergic reactions in some individuals.
(b) DEMI-PERMANENT DYES: These hair dyes penetrate the cuticle and cortex. They contain an oxidizing agent, have a more alkaline pH, and are, therefore, significantly longer lasting than the semipermanent hair dyes. Nevertheless, they are still not completely permanent and cannot lighten the original hair color.
(c) HAIR BLEACHES: These products are used to remove the hair color through a chemical reaction. They can be used alone or in combination with permanent hair colors.
(d) TEMPORARY HAIR DYES: These hair dyes are based chiefly on acid dyes and adhere to the outside of hair fibers by weak chemical bonds. These products are different from other products in that they are ‘leave-in’ products. After application, the hair is not rinsed and the color is washed out by the first shampooing.
(e) SEMI-PERMANENT DYES: These hair dye products adhere to the outside of hair fibers and partially penetrate the cuticle layers, making the hair dye longer lasting. Dark colors are obtained without the use of hydrogen peroxide. Hence there is no bleaching of the hair’s melanin, only masked with the colorant. Additionally, these products give some degree of highlighting effect and are colored slightly differently than the pigmented hair.
CHEMISTRY AND FORMULATION OF PARA PHENYLENE DIAMINE (PPD) BASED HAIR DYES
- The composition of permanent and demi-permanent dye products contain several, common and necessary ingredients such as dyes, surfactants, solvents, alkalizing agents, and oxidant.
- The dye intermediates are common and the chemistry of the dye-forming reactions is also the same.
- At the time of application, these dyes are colorless but turn to a particular color after undergoing chemical reactions on the hair.
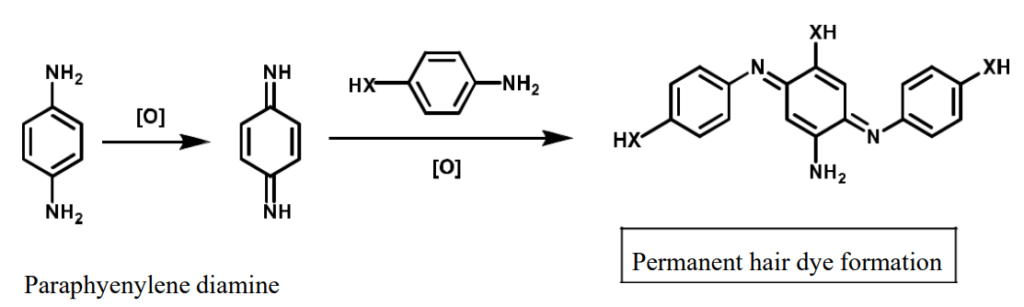
- Chemical reactions that take place in the color formation with PPD-based hair dyes are oxidation, coupling, and condensation in alkaline pH.
- The ingredients responsible for rendering these chemical reactions for color formation are bases, coupling agents, and oxidizing agents.
Bases: They are called “primary intermediates”. Chemically they are aromatic diamine compounds such as para-phenylenediamine or 2,5- diaminotoluene.
- Other useful primary intermediates are amino diphenylamines, amino methylphenols, and para-aminophenol.
- Primary intermediates undergo oxidation to produce highly reactive imines in the presence of “couplers”, and are able to form black or brown complexes with multiple nuclei by reacting with their unoxidized counterparts.
Coupling agents: They are aromatic in nature, and are referred to as “modifiers”. They are the derivatives of benzene which show – NH2 and – OH substitutions at the meta position.
- When used alone, primary intermediates provide a very limited shade range following their oxidation on hair.
- Hence, to enhance the range of available hair colors, the primary intermediates are oxidized in the presence of suitable “couplers”.
- While most couples do not produce colors when exposed to developers alone, they give a wide range of shades on hair when applied in combination with primary intermediates.
- Compounds used as coupling agents include 3-aminophenol, 2, 4- diaminoanisole, resorcinol, m-chlororesorcinol, and α naphthol and m-phenylenediamine and heterocyclics such as 2,6-diaminopyridine.
(a) Oxidizing agents: The commonly used oxidizing agent is hydrogen peroxide and known as “developer”.
(b)Oxidation dyes are produced directly on the hair by oxidizing aromatic PPD with an oxidizing agent hydrogen peroxide. The following chemical reaction takes place during the formation of PPD-based hair dye:
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on: Oral And Dental Care Products
