Methods of Preparation of Phenols: Phenol was initially obtained by fractional distillation of coal tar.
General Methods of Preparation of Phenols:
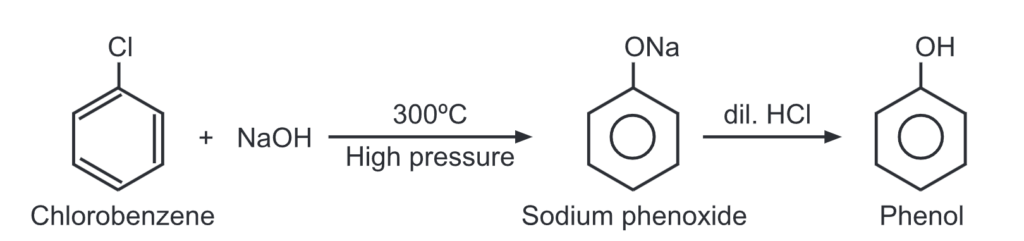
(a) Dows process: When chlorobenzene is heated with caustic soda at 300°C at 300 atm. pressure, sodium phenoxide is formed. It, upon acidification, gets converted to phenol.
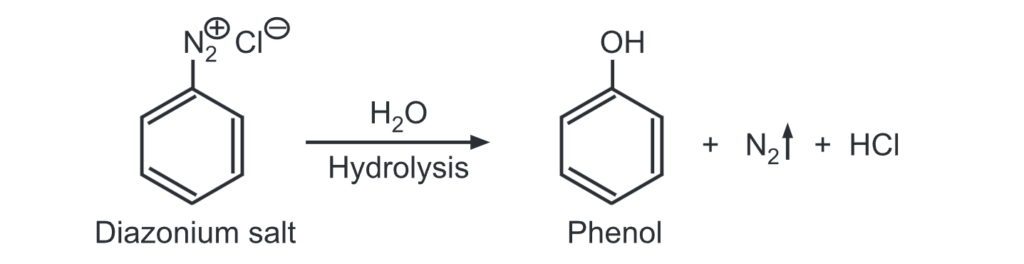
(b) From diazonium salt: A diazonium salt when warmed in presence of water, produces phenol.
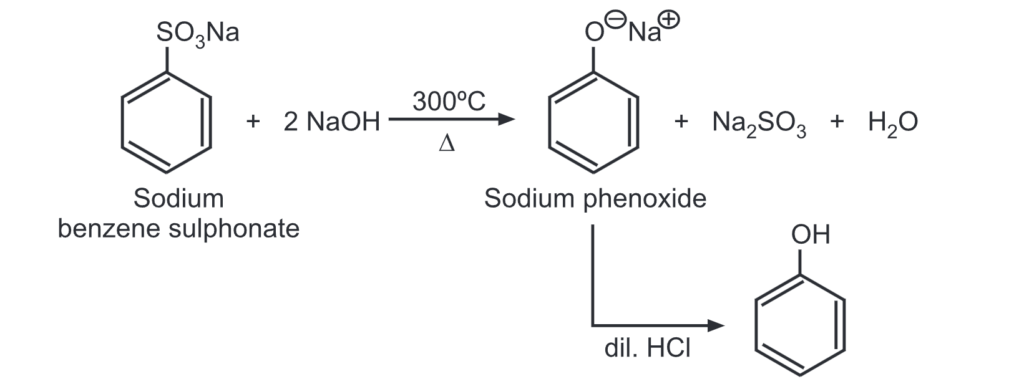
(c) From benzene sulphonate: When benzene sulphonate is heated with caustic soda at 300°C, sodium phenoxide is formed which upon acidification gives phenol.
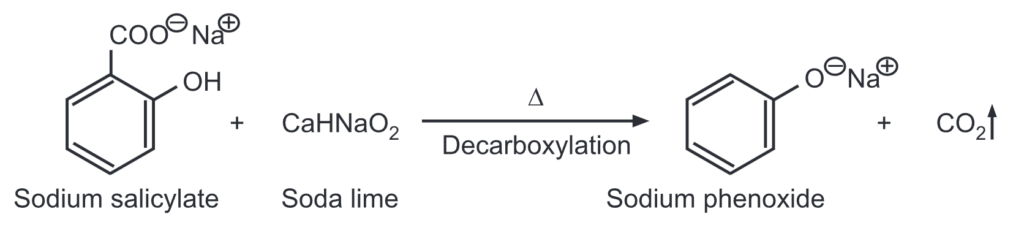
(d) From salicylic acid: Sodium salicylate when heated with soda lime undergoes decarboxylation to give sodium phenoxide which on acidification gives phenol.
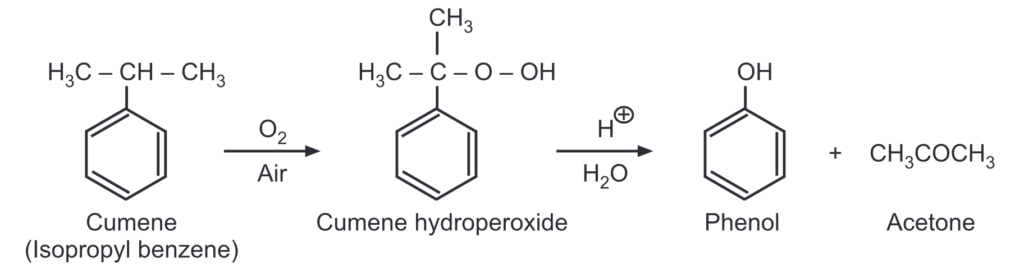
(e) Acidic oxidation of cumene: Cumene is oxidized in presence of air to give cumene hydroperoxide. The formation of cumene hydroperoxide proceeds by a free radical chain reaction.
The creation of the tertiary free radical is the initial step in the reaction.
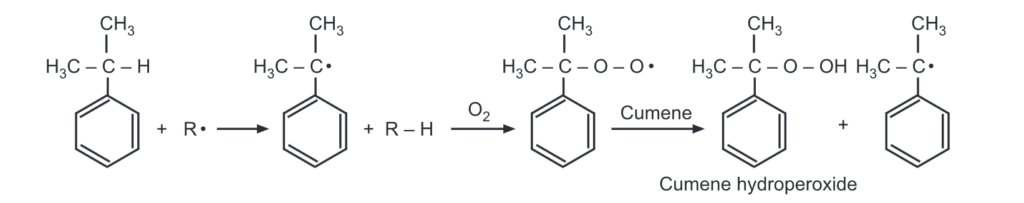
In the next step, the free radical is attached to the O2 molecule. Finally, the hydroperoxide free radical abstracts a hydrogen-free radical from a second molecule of cumene to form cumene hydroperoxide and a new tertiary free radical.
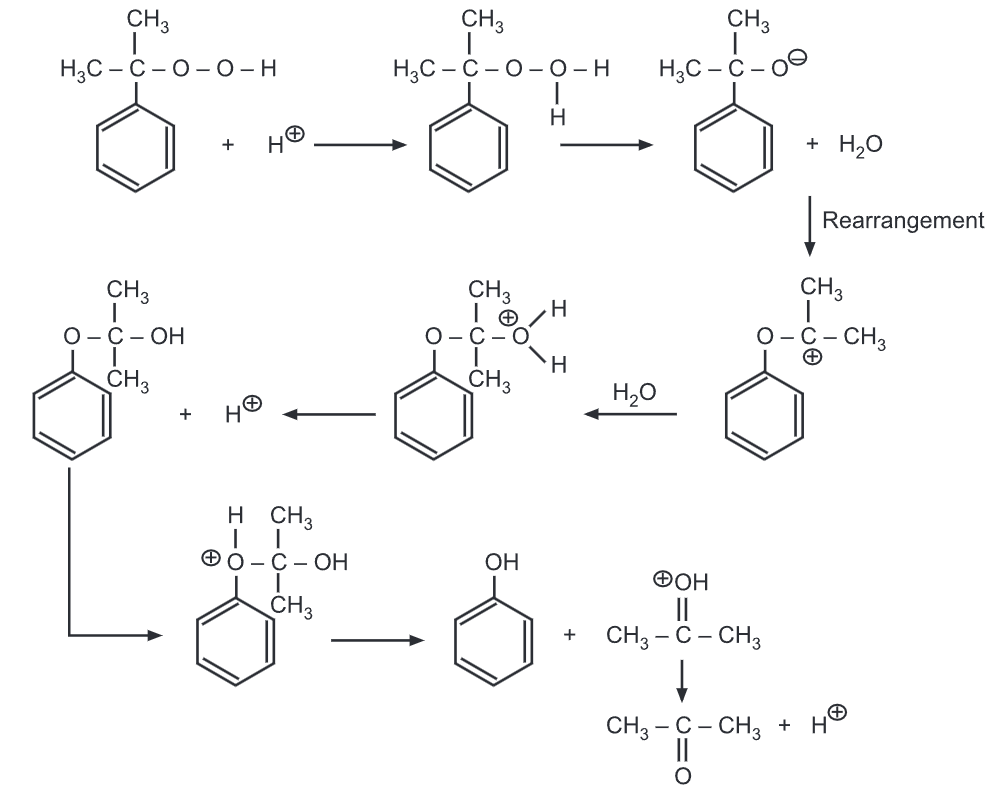
The degradation of cumene hydroperoxide proceeds via a carbocation mechanism.
(f) From benzene (Rachig’s method):
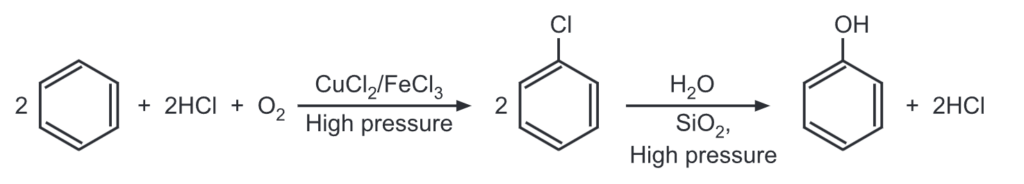
This method involves heating benzene, HCl, and air over a catalyst (mixture of CuCl2 and FeCl3) at high pressure of 500 K to give chlorobenzene which is then heated with superheated steam at high pressure of 750 K to give phenol.
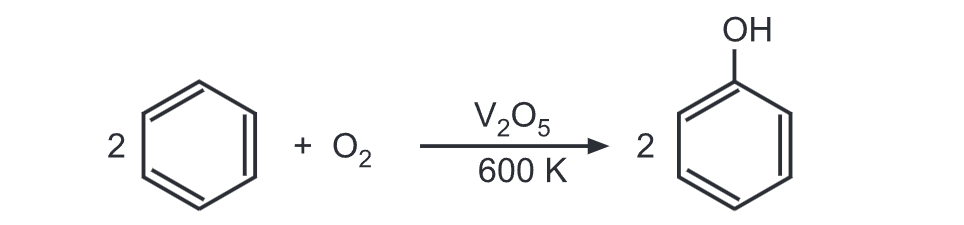
In yet another method, benzene and air are passed over V₂Os at 600 K. Benzene is thus oxidized to give phenol.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Diazo Coupling Reaction