Synthetic Uses of Aryl Diazonium Salts: Diazonium salts are prepared by treatment of aromatic amines with the nitrous acid generated in-situ from sodium nitrite and excess mineral acid. Diazonium compounds are not isolated and once prepared, they are used immediately in further reactions. Aryl diazonium salts have a wide range of synthetic applications.
For example, Diazonium salts are unstable but highly active intermediates used in the synthesis of a large variety of aromatic compounds.
Synthesis of Diazonium Salt
(a) Sandmeyer reaction (Aryl halides): Benzene diazonium salt heated with cuprous chloride or cuprous bromide respectively dissolved in HCI or HBr gives chlorobenzene or bromobenzene respectively.
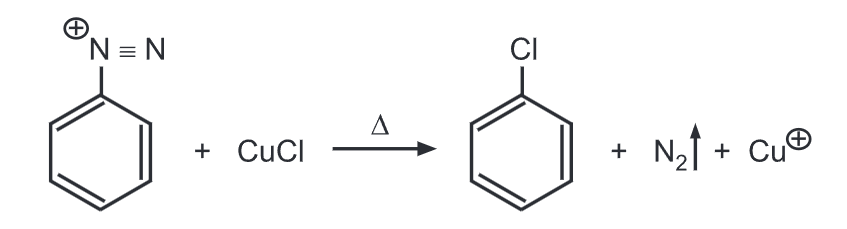
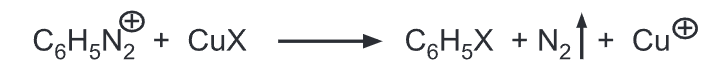
(b) Gatterman reaction (Aryl halides): Benzene diazonium salt is warmed with copper powder and HCl or HBr to produce chlorobenzene or bromobenzene respectively.
(c) Craig method: 2-Aminopyridine reacts with sodium nitrite, hydrobromic acid, and excess bromine to give 2-bromopyridine.
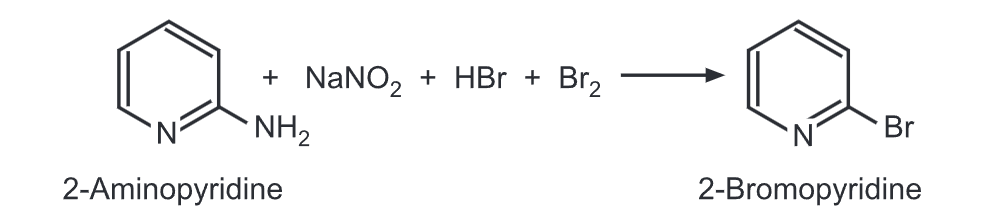
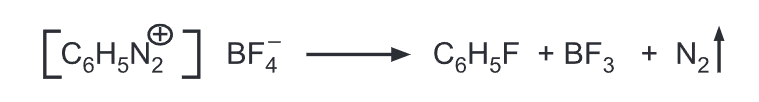
(d) Balz-Schiemann reaction: Fluorobenzene is produced by thermal decomposition of benzene diazonium fluoroborate.
(e) Replacement by nitro group: Benzene diazonium salt is treated with sodium nitrite in presence of copper to give nitrobenzene.

(f) Replacement by a hydroxyl group: Aqueous solution of aryl diazonium salt when heated to 100°C, gives phenols.

(g) Replacement by hydrogen: Aryldiazonium salts are reduced by hypophosphorous acid or sodium stannite to give benzene.
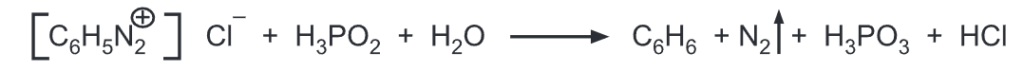
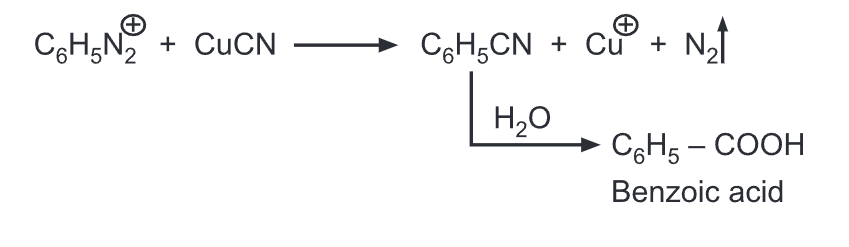
(h) Replacement by cyano group: When heated with cuprous cyanide, the diazonium salts are converted into respective aryl nitriles.
(i) Replacement by a thio group: Aryl diazonium salt is treated with potassium ethyl xanthate followed by hydrolysis gives thiophenol.

(j) Replacement by phenyl: Benzene diazonium salt is treated with benzene in the presence of sodium hydroxide gives diphenyl.
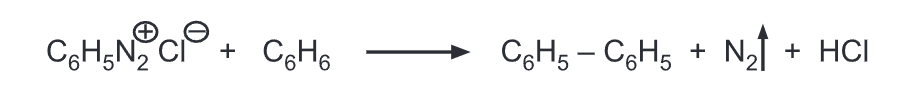
(k) Replacement by a carboxyl group: Aryl diazonium fluoroborate reacts with an aliphatic carboxylic acid and gives corresponding aromatic carboxylic acid.

(l) Meerwein arylation: Aryl diazonium salt reacts with compounds containing activated double bonds to give phenylated compounds.

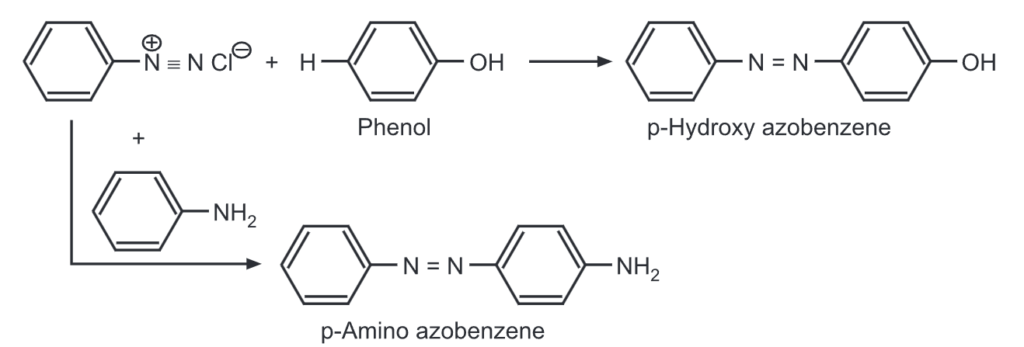
(m) Coupling reactions: Coupling reactions are electrophilic substitution reactions, where aryl diazonium salts are reacted with another aromatic compound to give azodyes.
e.g.,
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Basicity of Amines