It is a colorless to pale yellow low melting solid. Commercial diphenylmethane should be at least 97% pure. It must be free of halogens and have a minimum melting point of 240C. It is used as a fragrance in perfumes, soaps, and shampoo.
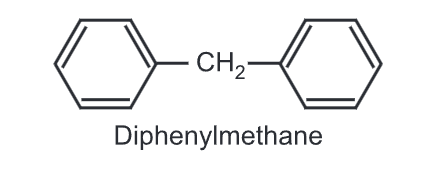
Chemical reactions of Diphenylmethane:
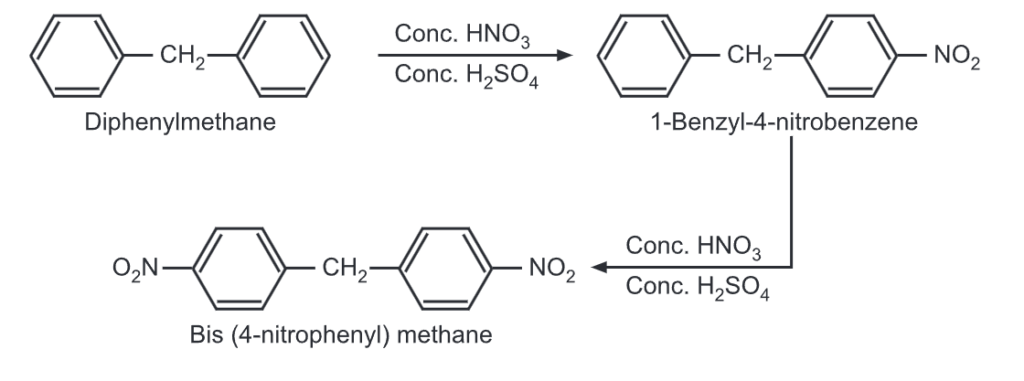
(i) Nitration: It undergoes nitration when heated with conc. HNO3/conc. H2SO4, mixture.
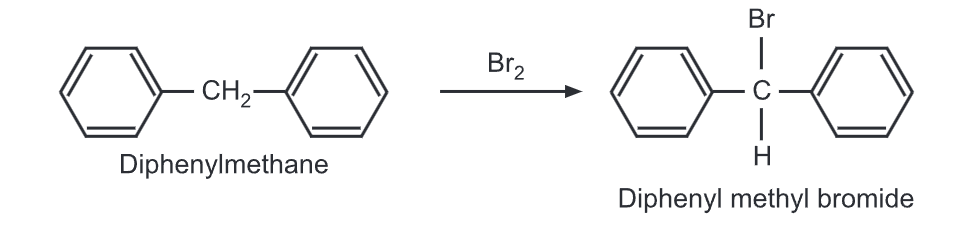
(ii) Halogenation: When treated with liquid bromine, it undergoes bromination at methane carbon.
(iii) Oxidation: Upon oxidation, diphenylmethane gives benzophenone.
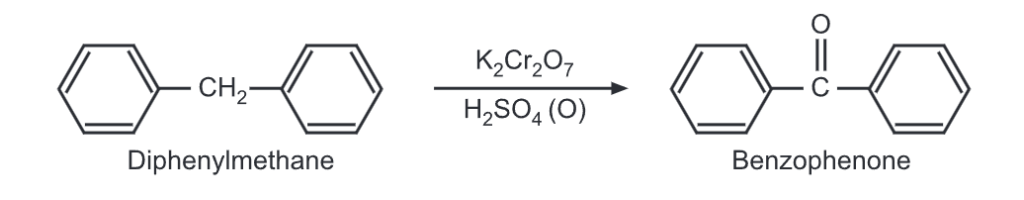
Synthesis of Diphenylmethane:
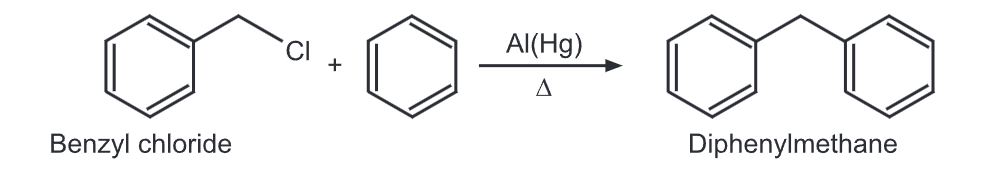
1) Diphenylmethane can be synthesized by Friedel Crafts’ alkylation of benzyl chloride with benzene in presence of amalgamated aluminum turning.
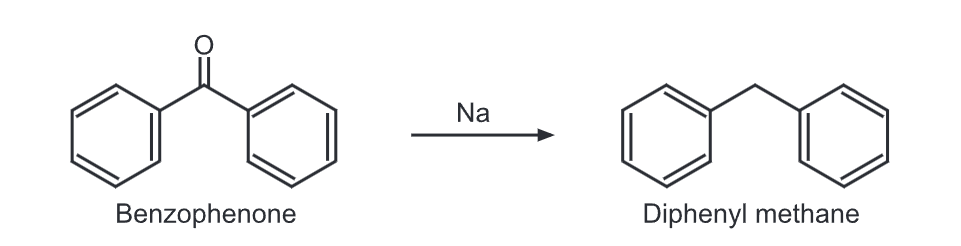
2) Diphenylmethariè can be synthesized by reduction of benzophenone using metallic sodium.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Polynuclear Hydrocarbons