Table of Contents
Principle of the falling film evaporator
In a falling film evaporator, feed enters from the top and flows down the walls of the tubes. The liquid gets heated rapidly due to heat transfer from steam. The liquid boils and becomes vapour, which forms small bubbles. They tend to fuse to form layers of bubbles, which travel down the tubes. Concentration takes place during this downward journey. Vapour and liquid are separated at the bottom.
Construction
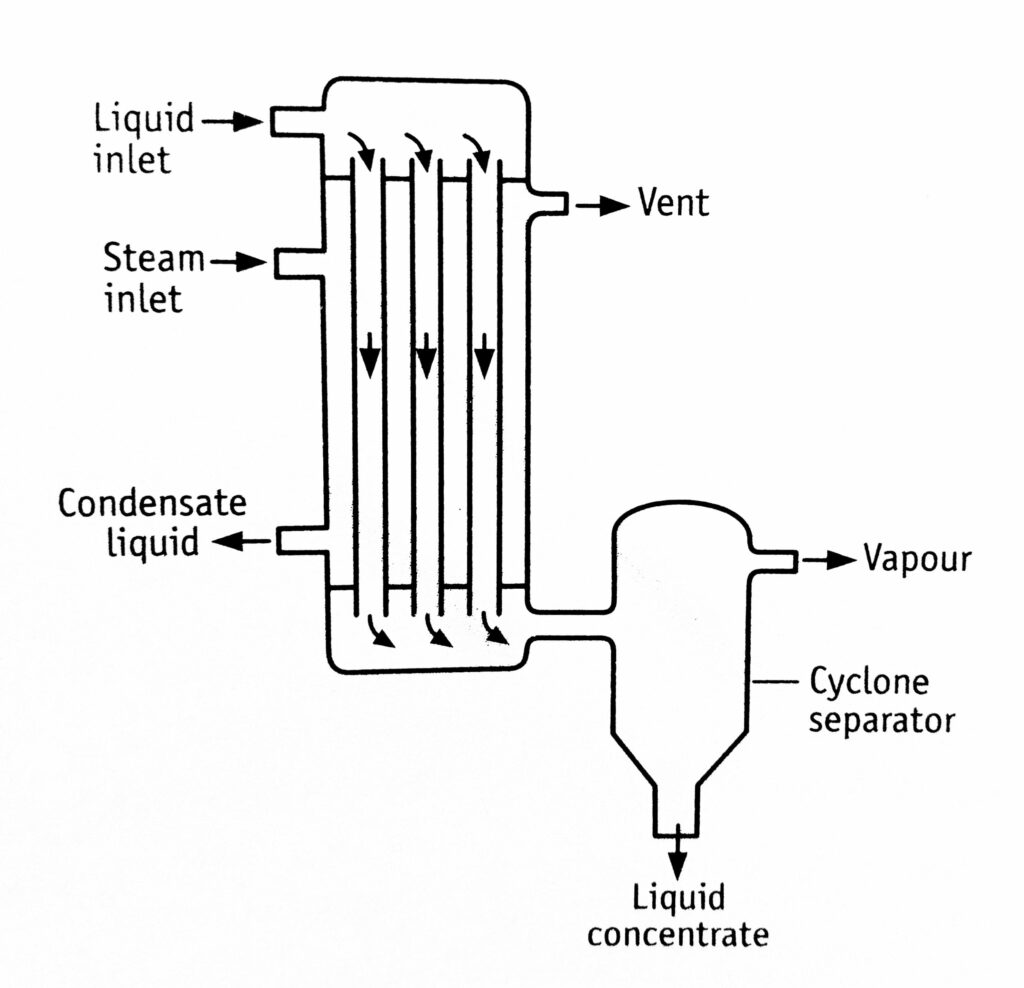
The construction of a falling film evaporator is shown in Figure 1.1. It resembles a climbing film evaporator but is inverted. In this evaporator, the heating unit consists of steam jacketed tubes. The feed inlet is from the top of the steam compartment. The other provisions are steam inlet, vent and condensate outlet remain same The outlet for the product is provided at the bottom and is connected to a cyclone separator.
Working on falling film evaporator
Steam is supplied into the steam compartment. Feed enters from the top of the tubes. The temperature of the boiling liquid is the same as that of the vapour head. The feed flows down the walls of the tubes. The liquid gets heated rapidly. The liquid boils and becomes vapour, which forms smaller bubbles. These tend to fuse to form layers of bubbles, which travel down the tubes. Concentration takes place during this downward journey. Vapour and liquid are separated in the cyclone separator.
Uses Falling film evaporator is used to separate volatile and non-volatile materials when the feed is of low viscosity. It is used for the concentration of yeast extract, manufacture of gelatin, and extracts of tea and coffee. It is also useful for concentrating heat-sensitive materials such as fruit juices.
Advantages:
- A falling film evaporator is suitable for high viscous liquids because the flow of vapour film is assisted by gravity.
- The liquid hold-up is less and the hold-up time is very small.
- The liquid is not overheated during passage and heat transfer coefficients are high even at low boiling temperature.
- Highly acidic and corrosive feeds can be concentrated using impervious graphite tubes and rubber lined vapour heads.
Disadvantages:
Easy distribution of feed to the individual tubes. be accomplished using a perforated plate above the tubes or using spray nozzles. Hence, it is not suitable for suspensions, as the solids clog the perforated plate. It is not suitable for salting or scaling liquids. The feed distribution in the tubes is poor. For a continuous supply, the liquid may be recirculated or the ratio of feed to evaporation is kept high.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Vertical Tube Evaporator