Furan Synthesis: Furan was first reported by Heinrich Limpricht in 1870. It is a colorless, inflammable, volatile, liquid with a boiling point of 31-32°C. The numbering and structures of furans are as follows:
Furan Chemical Synthesis
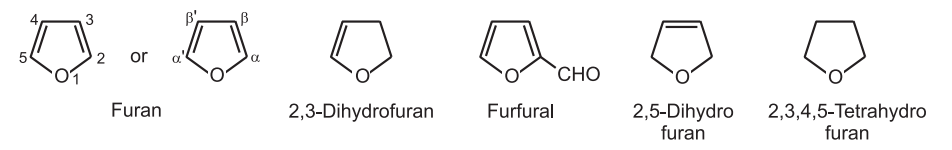
1. The vapor phase decarboxylation of furfural in the presence of palladium and charcoal gives furan.
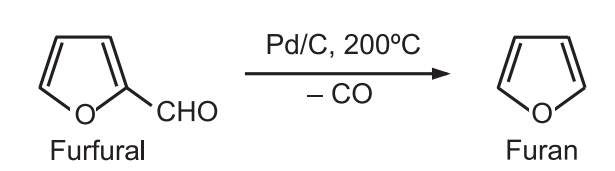
2. 1,3-Butadiene can be converted to furan by copper-catalyzed oxidation.
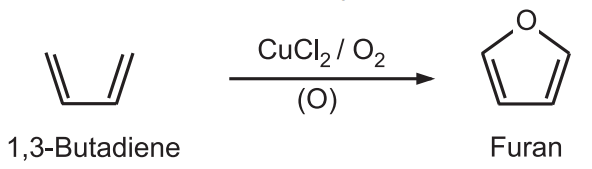
3. Paal-Knorr Synthesis: Under non-aqueous acidic conditions, 1, 4 – diketones undergo cyclization followed by dehydration to give furans.
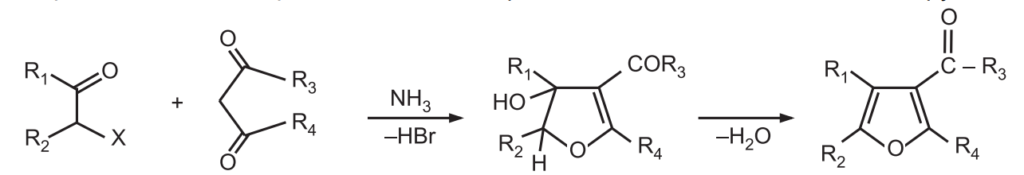
4. Fiest-Benary Synthesis: It is a condensation reaction between an α – halo ketone with a β – keto ester (or a β – diketone) in the presence of a base like ammonia or pyridine.
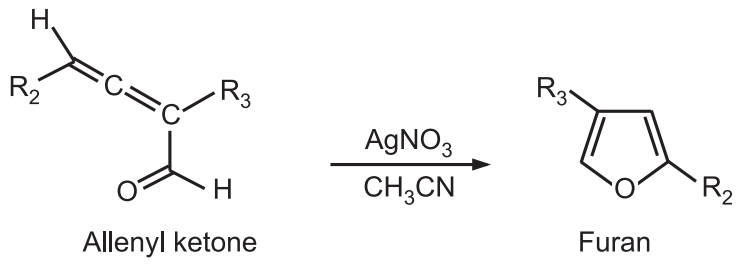
5. Allenyl ketones undergo cyclization in the presence of silver nitrate or silver boron tetrafluoride in CH3CN to give furans.
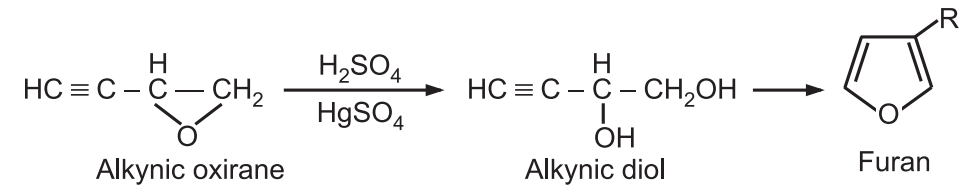
6. Ring expansion: Alkynic oxiranes when treated with sulfuric acid and mercury sulfate, undergo ring expansion to produce furans.
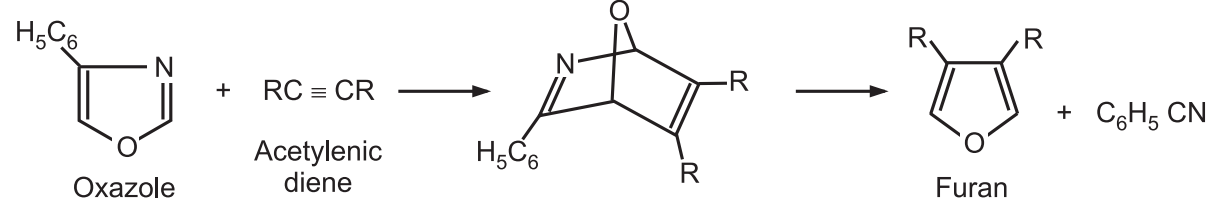
7. From other heterocycles: Oxazoles undergo Diels-Alder cycloaddition reaction with acetylenic dienophiles. The resulting product provides furan upon loss of nitrile.
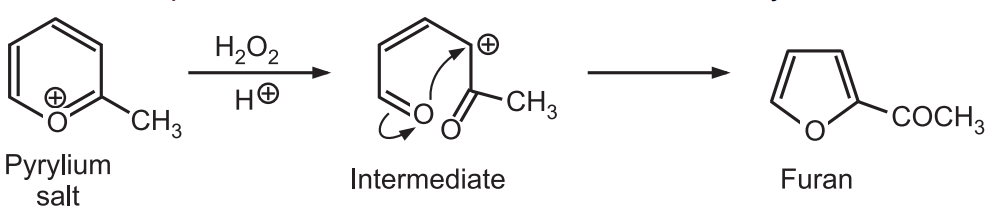
8. From Ring contraction: Oxidative ring contraction of pyrylium salts with aqueous hydrogen peroxide and perchloric acid leads to the formation of 2-acylfurans.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Pyrrole Chemical Reactions