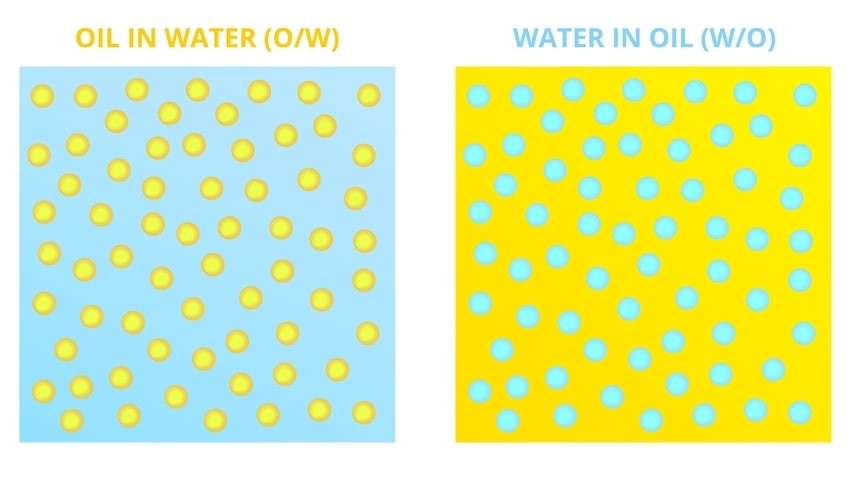
An emulsion is a liquid preparation containing two immiscible liquids, one of which is dispersed as globules (dispersed phase = internal phase) in the other liquid (continuous phase = external phase).
- Droplets ranging in diameter (0.1-100 um).
- An emulsion is thermodynamically unstable and is stabilized by the presence of emulsifying agent (emulgent or emulsifier).
- The emulsion is no more official in L.P. Emulsion protects the drug which is susceptible to hydrolysis and oxidation.
- It also provides prolonged action of the medication.
- In the form of an o/w emulsion, ephedrine has a more prolonged effect when applied to the nasal mucosa, than when used in an oily solution.
Types of Emulsion
A primary emulsion containing one internal phase, for example,
- oil-in-water emulsion (o/w)
- water-in-oil emulsion (w/o).
The secondary emulsion also called multiple-emulsion contains two internal phases, for instance,
- Oil in water/water in oil/ Oil in water
- Water in oil/Oil in water/ water in oil
It can be used to delay the release or to increase the stability of the active compounds.
Test for Emulsion
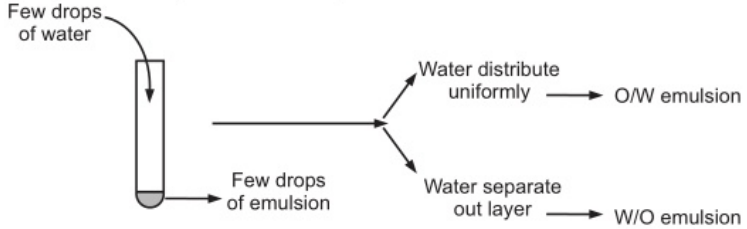
Dilution test: The addition of water to a w/o emulsion and oil to o/w emulsion would crack the emulsion and lead to the separation of the phases.
Conductivity test: When current is passed to an emulsion which is connected to a voltage bulb, the bulbs glow if it is o/w emulsion since water is a good conductor of electricity, and when the bulb does not glow it is w/o emulsion because oil is a non-conductor of electricity.
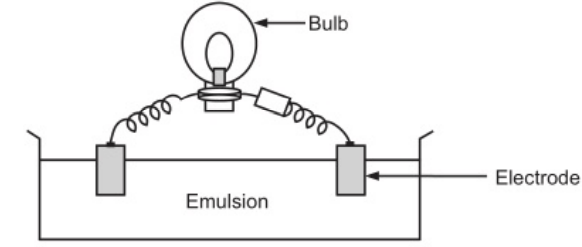
I.e.
o/w = current flow
w/o = current do not flow
o/w = current not flow (when purified water instead of portable water is taken).
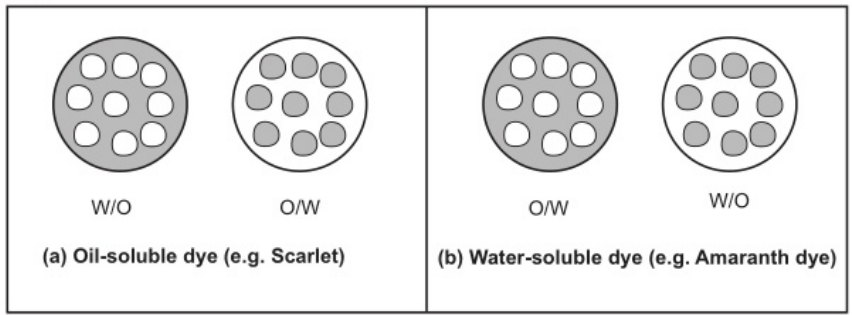
Dye test: Water-soluble dye will dissolve in the aqueous phase whereas oil-soluble dye will dissolve in the oil phase. For example Amaranth (0/w Emulsion), Scarlet/Sudan (w/o Emulsion).
Fluorescent test: Oils give fluorescence under UV light, while water does not. Therefore, O/W emulsion shows a spotty pattern while W/O emulsion fluorescence.
Filter paper test: o/w emulsion should spread out rapidly when dropped onto filter paper, in contrast, w/o will migrate slowly.
Cobalt chloride test: filter paper soaked in cobalt chloride (COCI) solution and allowed to dry, turn blue to pink on evaporation to o/w emulsion.
Pharmaceutical applications of emulsions
- To mask the bitter taste of the drugs.
- o/w emulsion is convenient means of oral administration of water-insoluble liquids.
- o/w emulsion facilitates the absorption of water-insoluble compounds compared to their oily solution preparations (e.g. vitamins).
- Oil-soluble drugs can be given parenterally in form of an oil-in-water emulsion. (e.g. Taxol)
- The emulsion can be used for external application in cosmetic and therapeutic uses.
Make sure you also check our other amazing Article on : Mouthwash